Baby’s oral health

Brushing
- Start brushing your baby’s teeth as soon as they come through the gum – usually at around 6 months old.
- Use a baby toothbrush and a tiny smear of family or baby toothpaste, containing at least 1000ppm fluoride.
- Don’t rinse your baby’s mouth after brushing.
- Brush your baby’s teeth twice a day – once at night and once during the day, usually in the morning.
NHS Oral health guidance for babies
Brushing for 0 to 3 year olds with Dr Ranj
Sugar
- Too much sugar can harm your baby’s new teeth.
- Only give water or milk to your baby to drink. Fresh fruit and vegetables provide your baby with all the sugar they need.
- Try not to give any food containing extra sugar – if you do, makde sure it is with a meal and not as a snack.
- Fresh fruit and vegetables are tooth-friendly snacks just like cheese, rice cakes, breadsticks and plain yogurt.
Dentist
National guidance advises that all babies should visit the dentist for the first time by their first birthday.Commonly used medicines after birth
Commonly used medicines after birth
1. Analgesics (pain killers)
a) Paracetamol (500mg tablets)
What is it used for? Paracetamol works by relieving pain and lowering high temperature. It can provide effective reliefnfrom mild to moderate pain, including headache, toothache, sore throat, symptomatic relief of rheumatic aches and pains, influenza symptoms and fever. How do I take it? Paracetamol can be taken regularly or when required for pain. Dosage: Adults and young persons aged 12 and over: take 2 tablets up to 4 times per day, as required. The tablets should be taken with water. Take only as much as you need to relieve symptom and leave at least 4 hours between each dose. Do not take more than 8 tablets in 23 hours. What are the side effects? Paracetamol is generally well-tolerated in most people. Is it safe to use while breastfeeding? Paracetamol is commonly used during breastfeeding.b) Co-dydramol
What is it used for? Co-dydramol (10/500 10mg dihydrocodeine and 500mg paracetamol) is a combination of paracetamol and dihydrocodeine. Dihydrocodeine is stronger than paracetamol and is used for the relief of mild to moderate pain. If you have had a caesarean section or moderate pain post-delivery, then you may be give a box of 30 tablets of co-dydramol on discharge from hospital. How do I take it? Dosage: Co-dydramol 1 to 2 tablets every 6 hours when required up to a maximum of 4 times per day. Do not take more than 8 tablets in 24 hours. We recommend that you step down pain relief and substitute these tablets for paracetamol as soon as possible which is usually after 3-4 days. Since these tablets contain paracetamol you should not take any other paracetamol tablets at the same time. Do not drink alcohol whilst taking co-dydramol. What are the side effects? The most common side effects of dihydrocodeine are drowsiness, constipation, feeling sick or dry mouth. You may be advised to take a gentle laxative if you experience constipation whilst taking co-dydramol. Is it safe to use during while breastfeeding? Dihydrocodeine can be used during breastfeeding as a pain killer where paracetamol has not been effective. Use the minimum effective does for the least amount of time. IMPORTANT: Although there is a small dose of dihydrocodeine in these co-dydramol tablets, if you are breastfeeding whilst taking it, inform your midwife immediately if your baby is showing signs of increased drowsiness, difficulty feeding, breathing problems or anything else unusual. Research has shown that some babies may be more susceptible than others to these side effects. If you would like any further information regarding the use of dihydrocodeine while breastfeeding, please discuss it with your midwife/doctor.c) Ibuprofen
What is it used for? Ibuprofen is anti-inflammatory drug used to treat inflammation in a variety of conditions. It is commonly used after birth to help ease pain and inflammation. How do I take it? Swallow tablets whole, with a glass of water. Take the tablets with, or after, food. Dosage: Adults: 400mg three times a day, 8 hours apart, is often prescribed after a procedure. If you have been given a diclofenac suppository after birth or a procedure, you cannot start ibuprofen until 18 hours later. The dose can be reduced to 200mg three times a day when the pain improves. Who should not use ibuprofen? Women with any of the following conditions should consult a doctor, midwife, or pharmacist before taking ibuprofen if there is history of:- asthma or breathing problems
- previous stomach ulcer
- previous reaction to aspirin, diclofenac and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- other medical conditions, e.g. kidney disease, heart disease, blood clotting disorders, liver disease.
- pass blood in your faeces (stools/motions)
- pass black tarry stools
- vomit blood or dark particles that look like coffee grounds
- suffer any allergic reaction such as itching, drowsiness, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, mouth or throat, which may in turn cause shortness of breath or difficult swallowing.
2. Ferrous Sulphate (Iron supplements)
What is it used for? Iron supplements are used to treat iron deficiency anaemia. When the body does not get enough iron, it cannot produce the number of normal red blood cells needed to keep you in good health. It is common for women who are pregnant or who have just given birth to have this condition. These medicines work by replacing body iron. Iron is a mineral that the body needs to produce red blood cells. How should I take it? Swallow the tablets who with water. Although iron preparations are best absorbed on an empty stomach, they may be taken after food to reduce the effects on the stomach. Iron supplements should not be taken within one hour before or two hours after eating or drinking the following products: tea, coffee, milk, eggs and wholegrains. These products can reduce the absorption of iron. Dosage: Ferrous sulphate 200 mg tablets Treatment of iron deficiency anaemia: 1 tablet 2-3 times a day Prevention of iron deficiency anaemia: 1 tablet per day What are the side effects? Like all medicines, ferrous sulphate tablets may cause side effects, the most common of which are constipation, diarrhoea, stomach pain, feeling sick and blackened stools (faeces). Is it safe to use during breastfeeding? Ferrous sulphate tablets are commonly used safely while breastfeeding. Ensure that you do not take more than the recommended dose. If you cannot tolerate ferrous sulphate tablets, an alternative is available called ferrous fumarate. This is available as a liquid or tablets. The same side effect and safety information applies as above for ferrous sulphate.3. Laxatives
What are they used for? Laxatives are used to treat constipation. What else can I do to prevent becoming constipated? The following hints are helpful in maintaining regular bowel habits:- Eat fibre-containing foods, e.g. wholegrain bread, fruit and vegetables.
- Drink sufficient liquid, preferably water.
- Take regular exercise.
a) Lactulose
Lactulose is a liquid laxative used to treat and prevent constipation. Lactulose can take 2-3 days to have an effect; it is generally considered to be a gentle laxative. Dosage: Usually 10 mls twice daily. It must be taken regularly to have an effect.b) Fybogel (Ispaghula husk)
Fybogel is a high fibre drink that works to increase the fibre in your diet. Increased fibre in the diet helps to gently relieve constipation. Fybogel is considered to be a gentle laxative. It is important to maintain an adequate intake of fluid whilst using Fybogel. Dosage: The usual dose is one sachet mixed with a glass of water, up to twice daily. Is it safe to use Lactulose or Fybogel after birth? Lactulose and Fybogel are not absorbed into the blood and only have a local effect on the gut. Both drugs are generally considered safe to use while breastfeeding, under the advice of a midwife or doctor.4. Blood clot prevention
Enoxaparin (also known as Clexane) is used to prevent blood clots. Blood clots usually present as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) usually in a leg vein, or pulmonary embolism (PE), a blood clot in the lung. Blood clots are more common during pregnancy and some women will be more at risk of blood clots than others. As well as prevention, enoxaparin is also used at higher doses for treatment of DVT and PE. Is it safe to use during breastfeeding? Enoxaparin is given as an injection just beneath the skin (subcutaneous). It is usually injected into a skin fold in your abdomen (stomach) or the upper part of your thigh. If this is not suitable, you may be advised to inject into an alternative site. It should not be injected into your muscles. It may be given either once or twice daily. You should adminster the dose at the time recommended by your doctor. How is exonaparin used after birth/caesarean section? If you have, or develop risk factors at the time of the birth, you may be started on enoxaparin. Examples of possible risk factors would be having a caesarean section or infection. If you were on enoxaparin during pregnancy, your doctor will want you to stay on the same treatment after the birth. They will inform you how long to continue this treatment. How to inject Enoxaparin (Clexane) You will be able to inject enoxaparin once you have been shown how to do so by your doctor or midwife, or by following the instruction leaflet that will be given to you upon discharge. It is a simple process and one that you can do at home. Follow these steps:- Wash and dry your hands.
- Clean the injection site. If someone else is doing it for you it is advisable that they wear gloves.
- Choose the injection site either on the outer aspect of your left or right thigh or your stomach if advised to do so. It is important that you change the site each time. If there is any oozing of blood at the injection site, apply gentle pressure. Do not rub as this may cause bruising.
- Dispose of the syringe in the yellow sharps box provided. This box should be kept out of the reach of other people.
Commonly used medicines during pregnancy
Commonly used medicines during pregnancy

1. Analgesics (pain killers)
a) Paracetamol (500mg tablets)
What is it used for? Paracetamol is a commonly used pain killer in pregnancy. Paracetamol works by relieving pain and lowering high temperature. It can provide effective relief from mild to moderate pain, including headache, toothache, sore throat, symptomatic relief of rheumatic aches and pains, influenza symptoms and fever. How do I take it? Paracetamol can be taken regularly or when required for pain. Dosage: Adults and young persons aged 12 and over: take 2 tablets up to 4 times per day, as required. The tablets should be taken with water. Take only as much as you need to relieve symptom and leave at least 4 hours between each dose. Do not take more than 8 tablets in 23 hours. What are the side effects? Paracetamol is generally well-tolerated in most people. Is it safe to use during pregnancy? Paracetamol is commonly used during pregnancy.b) Co-dydramol
What is it used for? Co-dydramol (10/500 10mg dihydrocodeine and 500mg paracetamol) is a combination of paracetamol and dihydrocodeine. Dihydrocodeine is stronger than paracetamol and is used for the relief of mild to moderate pain. How do I take it? Dosage: Co-dydramol 1 to 2 tablets every 6 hours when required up to a maximum of 4 times per day. Do not take more than 8 tablets in 24 hours. We recommend that you step down pain relief and substitute these tablets for paracetamol as soon as possible which is usually after 3-4 days. Since these tablets contain paracetamol you should not take any other paracetamol tablets at the same time. Do not drink alcohol whilst taking co-dydramol. What are the side effects? The most common side effects of dihydrocodeine are drowsiness, constipation, feeling sick or dry mouth. You may be advised to take a gentle laxative if you experience constipation whilst taking co-dydramol. Is it safe to use during pregnancy? Use of dihydrocodeine during pregnancy as a pain killer can be justified where paracetamol has not been effective. Use the minimum effective does for the least amount of time. If you would like any further information regarding the use of dihydrocodeine in pregnancy, please discuss it with your midwife/doctor.2. Ferrous Sulphate (Iron supplements)
What is it used for? Iron supplements are used to treat iron deficiency anaemia. When the body does not get enough iron, it cannot produce the number of normal red blood cells needed to keep you in good health. It is common for women who are pregnant or who have just given birth to have this condition. These medicines work by replacing body iron. Iron is a mineral that the body needs to produce red blood cells. How should I take it? Swallow the tablets who with water. Although iron preparations are best absorbed on an empty stomach, they may be taken after food to reduce the effects on the stomach. Iron supplements should not be taken within one hour before or two hours after eating or drinking the following products: tea, coffee, milk, eggs and wholegrains. These products can reduce the absorption of iron. Dosage: Ferrous sulphate 200 mg tablets Treatment of iron deficiency anaemia: 1 tablet 2-3 times a day Prevention of iron deficiency anaemia: 1 tablet per day What are the side effects? Like all medicines, ferrous sulphate tablets may cause side effects, the most common of which are constipation, diarrhoea, stomach pain, feeling sick and blackened stools (faeces). Is it safe to use during pregnancy? Ferrous sulphate tablets are commonly used safely in pregnancy. Ensure that you do not take more than the recommended dose. If you cannot tolerate ferrous sulphate tablets, an alternative is available called ferrous fumarate. This is available as a liquid or tablets. The same side effect and safety information applies as above for ferrous sulphate.3. Laxatives
What are they used for? Laxatives are used to treat constipation. Pregnant women may experience constipation, which can be very uncomfortable. This is because the whole digestive system is influenced by hormonal changes during pregnancy. It is important for pregnancy women to look after their diet and maintain regular bowel habits to avoid unnecessary discomfort. What else can I do to prevent becoming constipated? The following hints are helpful in maintaining regular bowel habits:- Eat fibre-containing foods, e.g. wholegrain bread, fruit and vegetables.
- Drink sufficient liquid, preferably water.
- Take regular exercise.
a) Lactulose
Lactulose is a liquid laxative used to treat and prevent constipation. Lactulose can take 2-3 days to have an effect; it is generally considered to be a gentle laxative. Dosage: Usually 10 mls twice daily. It must be taken regularly to have an effect.b) Fybogel (Ispaghula husk)
Fybogel is a high fibre drink that works to increase the fibre in your diet. Increased fibre in the diet helps to gently relieve constipation. Fybogel is considered to be a gentle laxative. It is important to maintain an adequate intake of fluid whilst using Fybogel. Dosage: The usual dose is one sachet mixed with a glass of water, up to twice daily. Is it safe to use Lactulose or Fybogel during pregnancy? Lactulose and Fybogel are not absorbed into the blood and only have a local effect on the gut. Both drugs are generally considered safe to use in pregnancy and for breastfeeding, under the advice of a midwife or doctor.4. Blood clot prevention
Enoxaparin (also known as Clexane) is used to prevent blood clots. Blood clots usually present as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) usually in a leg vein, or pulmonary embolism (PE), a blood clot in the lung. Blood clots are more common during pregnancy and some women will be more at risk of blood clots than others. Your risk factors for developing a blood clot will be assessed at your booking appointment and if you are admitted to the hospital. As well as prevention, enoxaparin is also used at higher doses for treatment of DVT and PE. How is enoxaparin used during pregnancy? During the antenatal period, your midwife or obstetrician will assess your risk of developing a DVT/PE. They will look at your previous history and other risk factors that may exist. Your obstetrician will then decide if you require enoxaparin during pregnancy, and the dose you are to have. Is it safe to use during pregnancy? Enoxaparin is given as an injection just beneath the skin (subcutaneous). It is usually injected into a skin fold in your abdomen (stomach) or the upper part of your thigh. If this is not suitable, you may be advised to inject into an alternative site. It should not be injected into your muscles. It may be given either once or twice daily. You should administer the dose at the time recommended by your doctor. How to inject Enoxaparin (Clexane) You will be able to inject enoxaparin once you have been shown how to do so by your doctor or midwife, or by following the instruction leaflet that will be given to you upon discharge. It is a simple process and one that you can do at home. Follow these steps:- Wash and dry your hands.
- Clean the injection site. If someone else is doing it for you it is advisable that they wear gloves.
- Choose the injection site either on the outer aspect of your left or right thigh or your stomach if advised to do so. It is important that you change the site each time. If there is any oozing of blood at the injection site, apply gentle pressure. Do not rub as this may cause bruising.
- Dispose of the syringe in the yellow sharps box provided. This box should be kept out of the reach of other people.
Baby car seats and slings
Baby car seats and slings
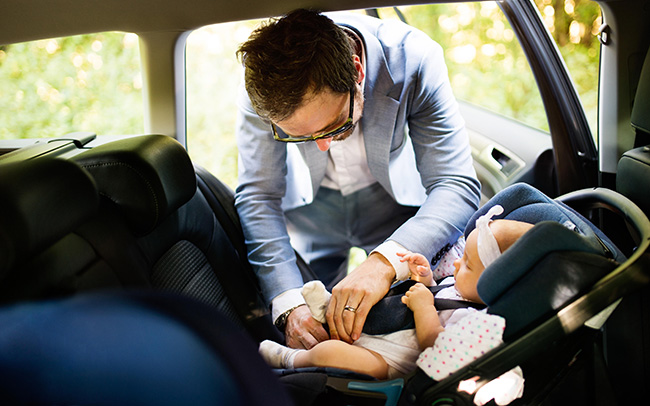 When travelling by car it is essential to place your baby in a suitable baby car seat. You will need the car seat to take your newborn baby home from hospital, so it is worth taking the time to find a suitable car seat during pregnancy.
Many parents also choose to carry their baby in a sling. The guidance in the link below shows how to do this safely.
When travelling by car it is essential to place your baby in a suitable baby car seat. You will need the car seat to take your newborn baby home from hospital, so it is worth taking the time to find a suitable car seat during pregnancy.
Many parents also choose to carry their baby in a sling. The guidance in the link below shows how to do this safely.
Heart health after giving birth
Heart health after giving birth
 Chest pain in pregnancy and/or after your baby’s birth should never be ignored. Some chest pain can be serious and can head to a heart attack, heart failure, cardiac arrest or even death. Most women do not suffer from these conditions during or after pregnancy but it is important to recognise the symptoms and, if you have any of them, to seek treatment quickly.
Chest pain in pregnancy and/or after your baby’s birth should never be ignored. Some chest pain can be serious and can head to a heart attack, heart failure, cardiac arrest or even death. Most women do not suffer from these conditions during or after pregnancy but it is important to recognise the symptoms and, if you have any of them, to seek treatment quickly.
Pre-exisiting heart conditions
If you have a known heart condition, were born with a congenial heart defect or have been diagnosed with heart disease, your midwife/GP/cardilogist will monitor your heart health before, during and after pregnancy.Symptoms of a heart attack can include:
- central chest pain
- arm pain or numbness
- pain in the jaw, back or shoulders
- nausea
- sweating/clamminess
- breathing difficulties
When should I contact the midwife or doctor?
If you feel unwell, contact your midwife or GP for guidance. If you experience some/all of the above symptoms, dial 999 and ask for an ambulance as yoru heart health needs to be investigated quickly. An ECG monitor and a troponin blood test should be carried out to find out if you have had a heart attack.When am I more likely to have a heart attack?
You are more likely to have a heart attack if you:- have a family history of heart problems
- have high blood pressure
- have high cholesterol
- smoke
- drink excessively
- are obese
Heart health in pregnancy
Heart health in pregnancy
 Chest pain in pregnancy and/or afer your baby’s birth should never be ignored. Some chest pain can be serious and can lead to a heart attack, heart failure, cardiac arrest or even death. Most women do not suffer from these conditions during or after pregnancy but it is important to recognise the symptoms and, if you have any of them, to seek treatment quickly.
Chest pain in pregnancy and/or afer your baby’s birth should never be ignored. Some chest pain can be serious and can lead to a heart attack, heart failure, cardiac arrest or even death. Most women do not suffer from these conditions during or after pregnancy but it is important to recognise the symptoms and, if you have any of them, to seek treatment quickly.
Pre-existing heart conditions
If you have a known heart condition, were born with a congenital heart defect or have been diagnosed with heart disease, you should tell your midwife/GP/cardiologist and they will monitor your heart health before, during and after pregnancy and your health.Symptoms of health attack can include:
- Central chest pain
- Arm pain or numbness
- Pain in the jaw, back or shoulders
- Nausea
- Sweating/clamminess
- Breathing difficulties
When should I contact the midwife or doctor?
If you feel unwell, contact your midwife or GP for guidance. If you experience some/all of the above symptoms, dial 999 and ask for an ambulance as your heart health needs to be investigated quickly. An ECG monitor and a troponin blood test should be carried out to find out if you have had a heart attack.When am I more likely to have a heart attack?
You are more likely to have a heart attack if you:- have a family history of heart problems
- have high blood pressure
- have high cholesterol
- smoke
- drink excessively
- are obese
